THE GEORGE EASTMAN MUSEUM in Rochester, New York, is, like most museums, full of historically significant and wonderfully nerdy objects. The museum’s namesake, George Eastman, founded the Eastman Kodak company at the turn of the 20th century and revolutionized photographic film in 1888 in a way that made photography accessible to the general public, so they would no longer be forced to sit in front of a professional or learn complex chemistry. He died in 1932, but the museum was founded in 1947. The collection now contains authentic Ansel Adams prints, a number of very rare (and extremely flammable) early-20th-century nitrate cinema film reels, and a smattering of cameras and photographic accessories from way before digital photography. The true treasures, however, live in the subbasement, in the technology collection.
Descend three flights of stairs in the middle of the atrium and you’ll find yourself in a time capsule of offices adorned in the same turquoise-and-pink color scheme you’d find in an early-’90s Taco Bell. From there, pass through a double-door climate lock into one of the world’s most comprehensive and impressive collections of photography and cinema gear, with more than 10,000 cameras and 20,000 objects in total.
Curator of technology Todd Gustavson has been in charge of the collection since it moved into its current home in 1989 (hence the interior design choices). Many of the pieces came directly from Kodak’s former technology archive in the basement of the Eastman House. Since then, new additions have come from private gifts, public auctions, and even eBay. Gustavson gave us an opportunity to see some of the most intriguing, historically significant, and just plain weird pieces in the archive.
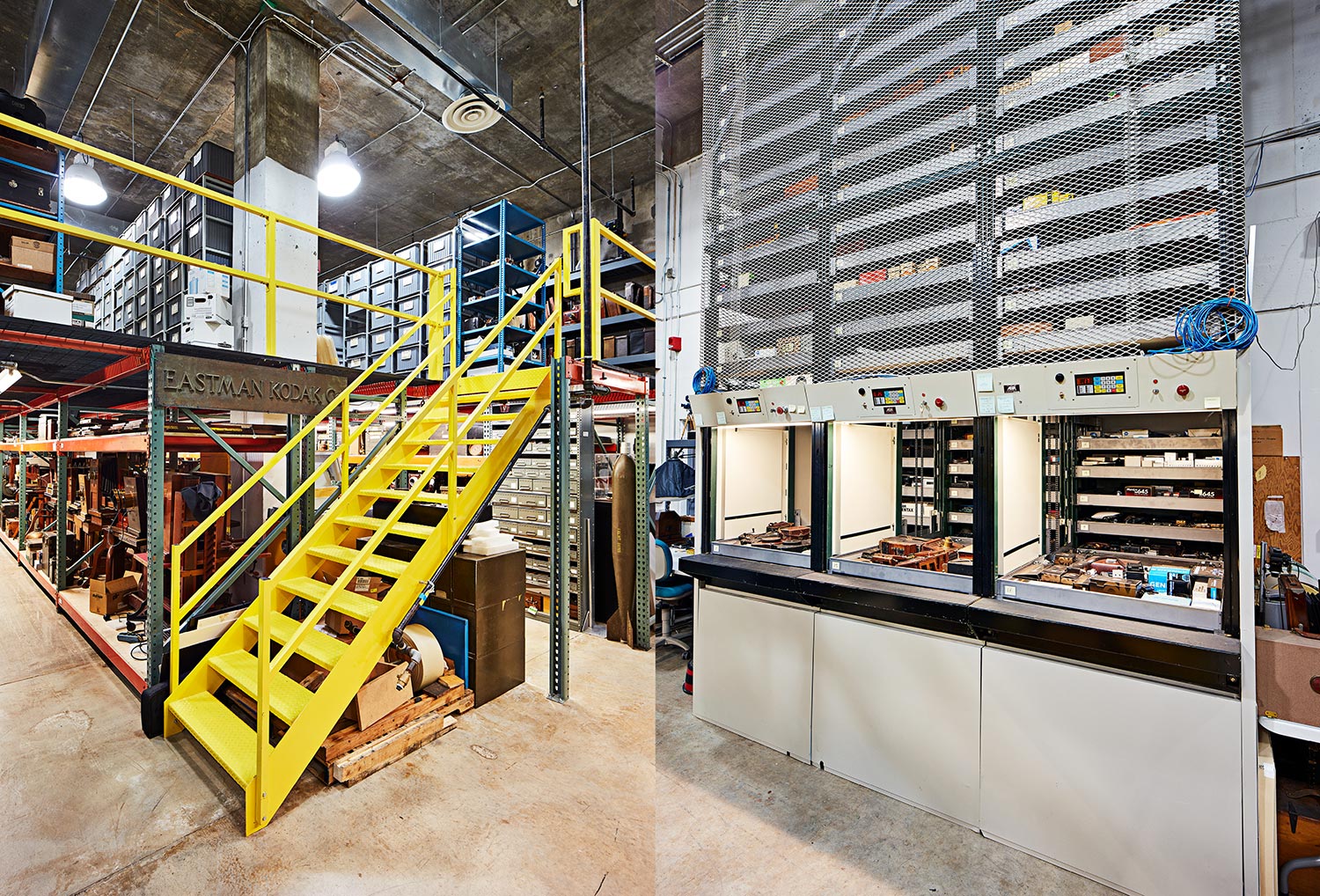

↑ The space itself boasts a roughly 5,000-square-foot main floor, as well as an elevated 3,000-square-foot mezzanine that was added in the early 2010s. It’s kept at 62 degrees with 45 percent humidity. That climate strikes a balance that’s dry enough to prevent fungus from growing but moist enough to prevent dry rot and keep the lubricating oil in the cameras from turning to sticky tar. A two-story motorized storage system holds thousands of cameras on trays in a revolving carousel. It’s like a massive vending machine full of photography gear.
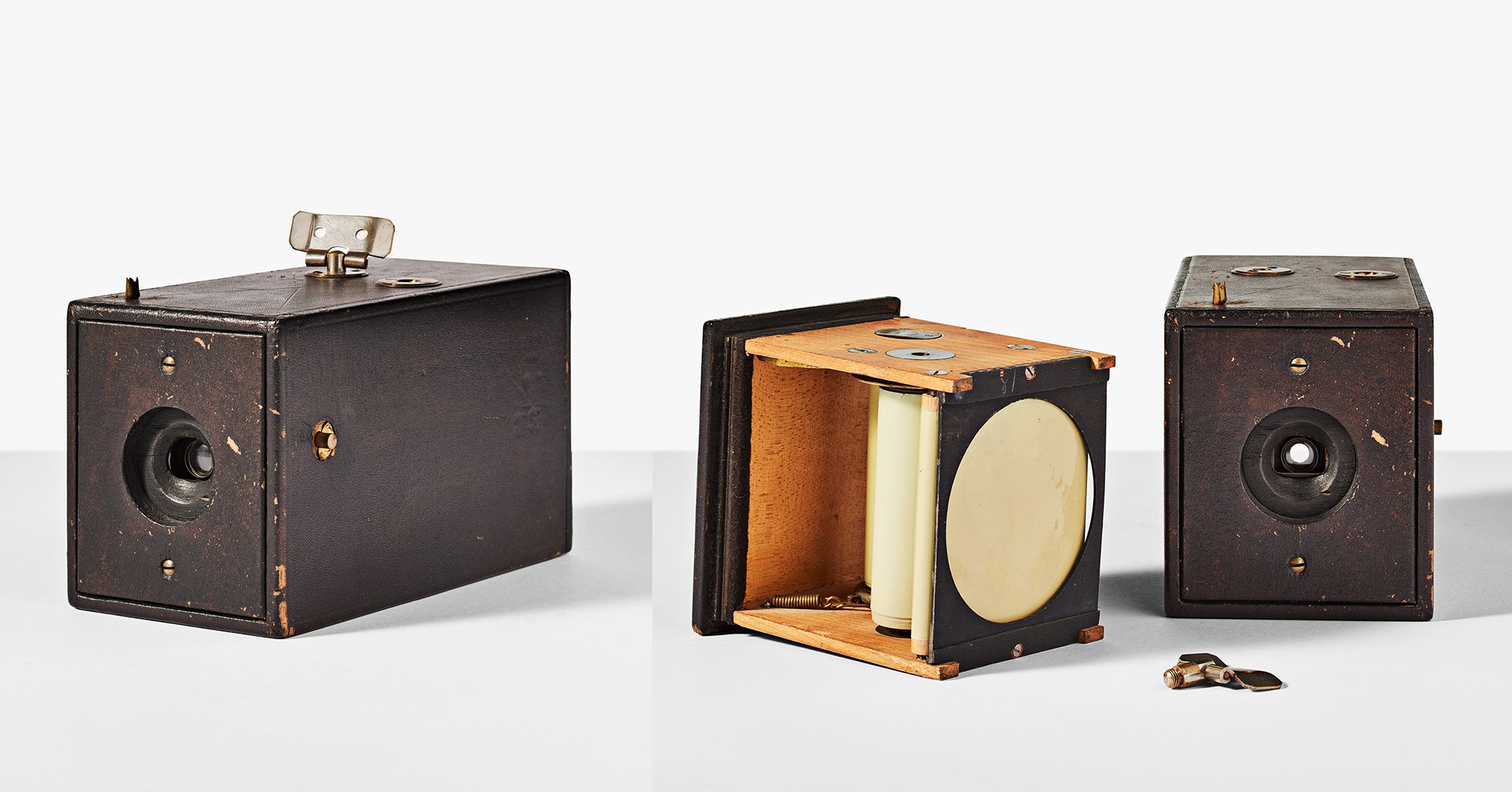

↑ In 1888, George Eastman released roughly 5,000 units of the original Kodak camera with a clever slogan: “You press the button, we do the rest.” The camera cost $25 at the time (roughly $800 in 2023 dollars) and came preloaded with enough film for 100 shots. Once the film was exposed, customers would return the camera to a shop to get their prints and a reload of film for $10, roughly $300 in today’s money. It was a revolutionary concept that brought about the age of snapshot photography by drastically simplifying the process.
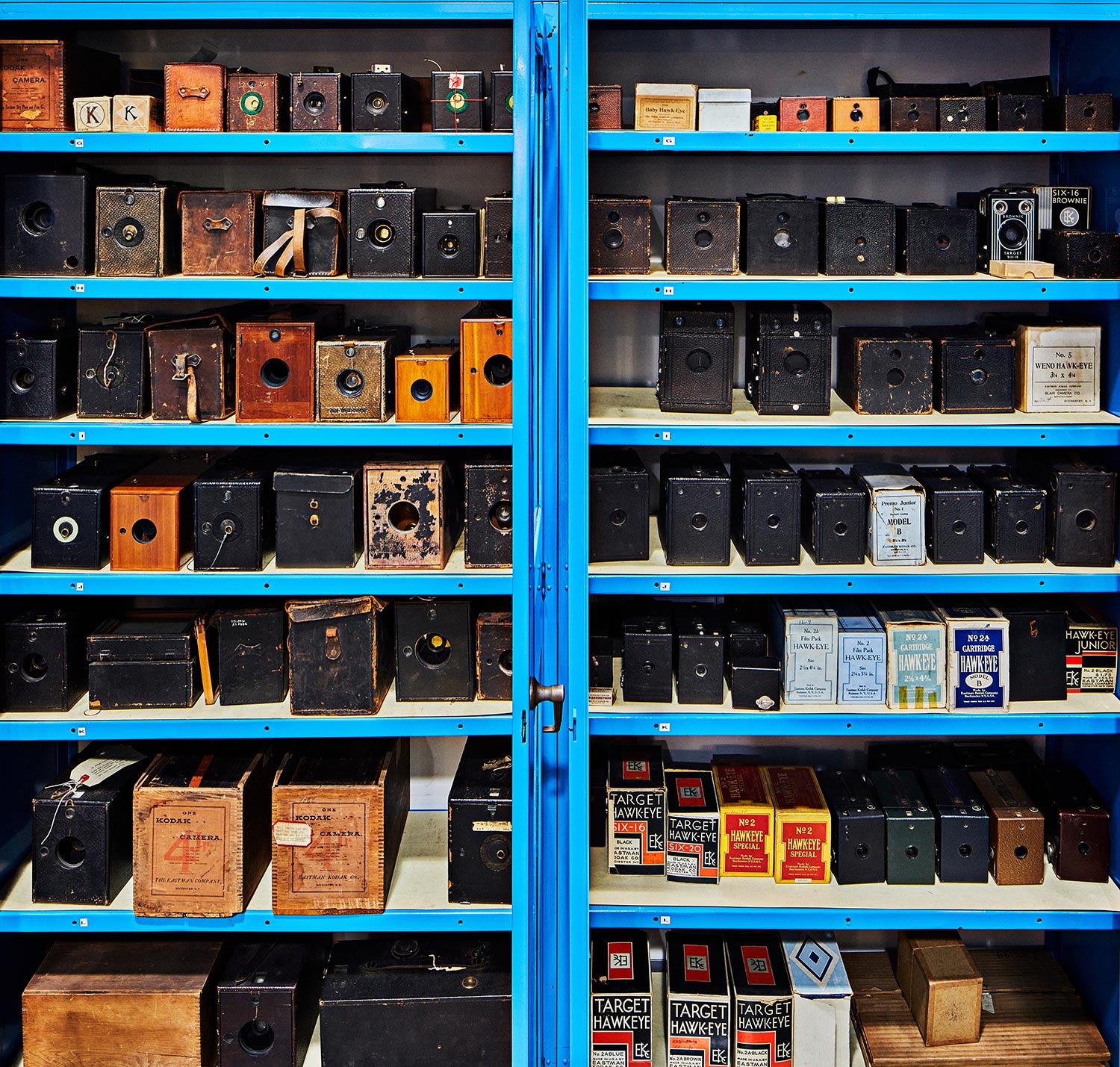

↑ You’ve likely seen box cameras at antique stores and estate sales, as hundreds of models hit the market in the years after the original Kodak debuted. The Eastman collection contains hundreds of them spanning decades. Some are wood, while others are made of cardboard or a type of plastic called Bakelite, which was popular approaching the middle of the 20th century. The two small boxes with K’s neatly cataloged in the top left are extremely rare early rolls of Kodak film that would be the centerpiece of a typical camera collection.
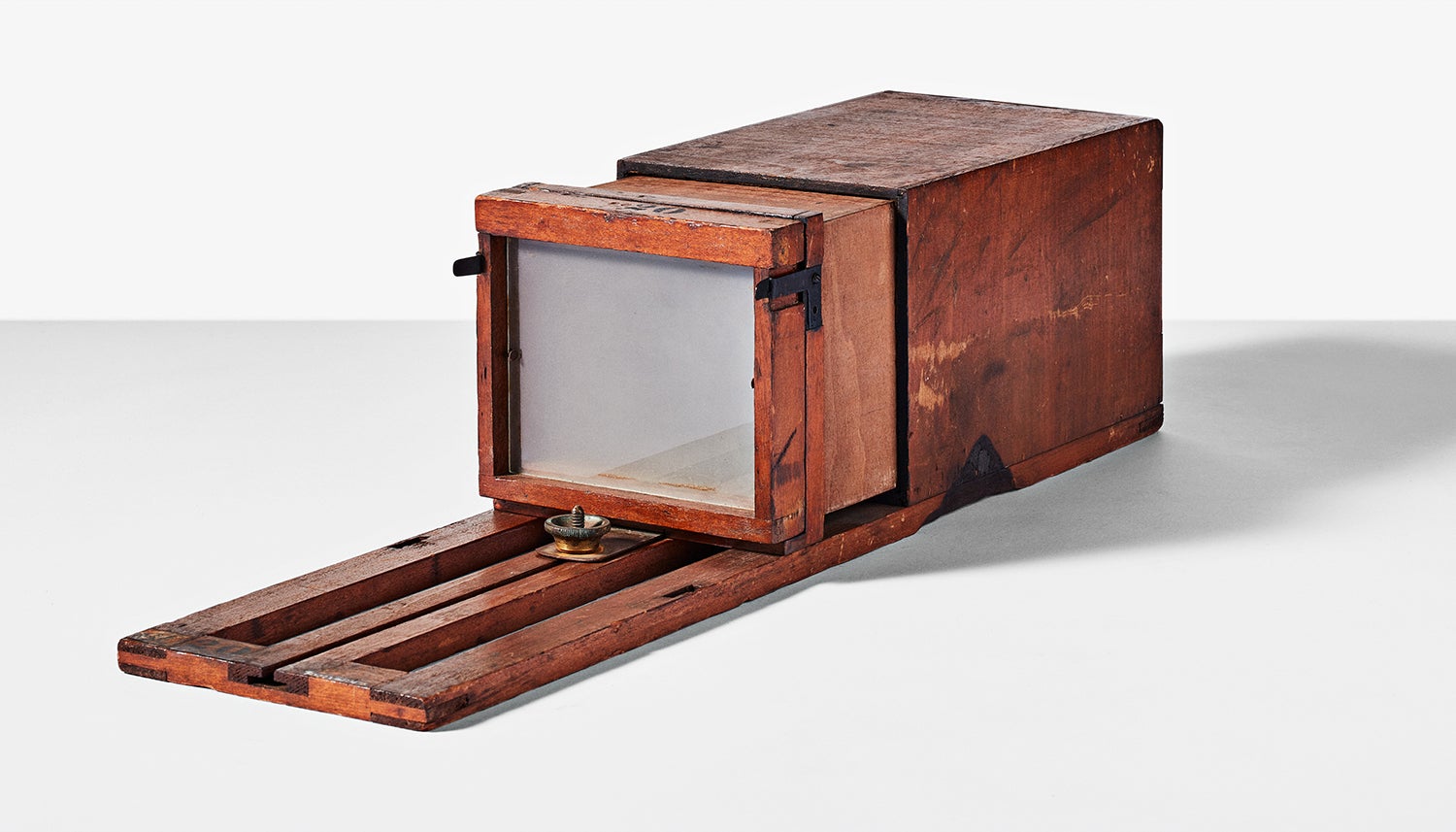

↑ This Scovill Manufacturing Company camera doesn’t have a lens or a shutter mechanism, but it holds a special place in both photographic and scientific history. It’s one of 24 cameras that Eadweard Muybridge used in the 1880s during his endeavors to capture animal locomotion. A horse would trigger a tripwire attached to each camera’s elaborate shutter mechanism as it sped by to capture a sequence of images. Presented in rapid succession, the glass plates would create the illusion of continuous motion. This process laid the groundwork for the original motion pictures. The Eastman collection actually has three of these.
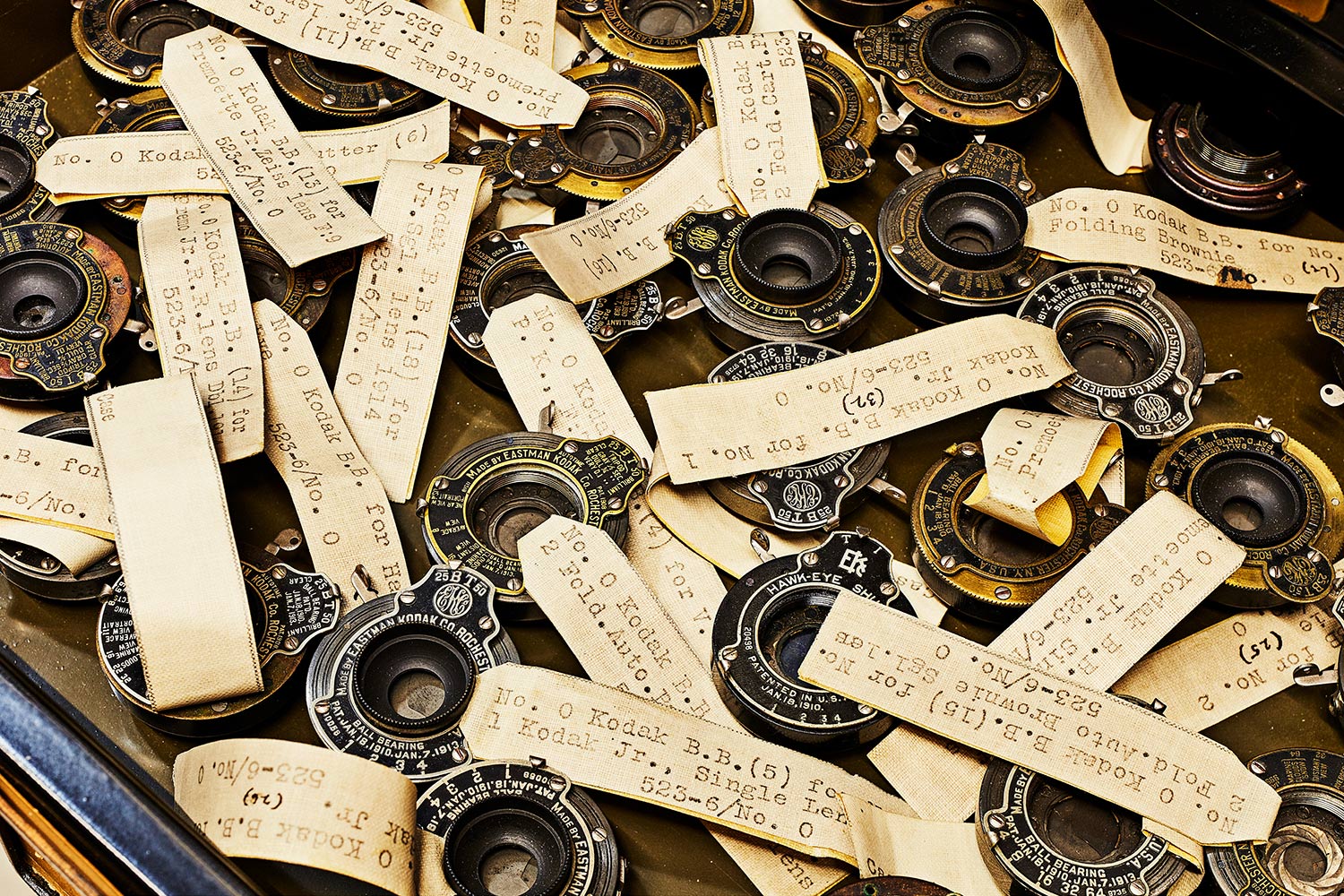

↑ This drawer contains numerous examples of shutter mechanisms from various Kodak cameras produced roughly a century ago. The shutter is the mechanical part of the camera that opens and closes in order to control how much light comes in and hits the film, and Kodak kept an example of every version of its devices in order to track the technology as it advanced. Each has its original label with part numbers and patent info.
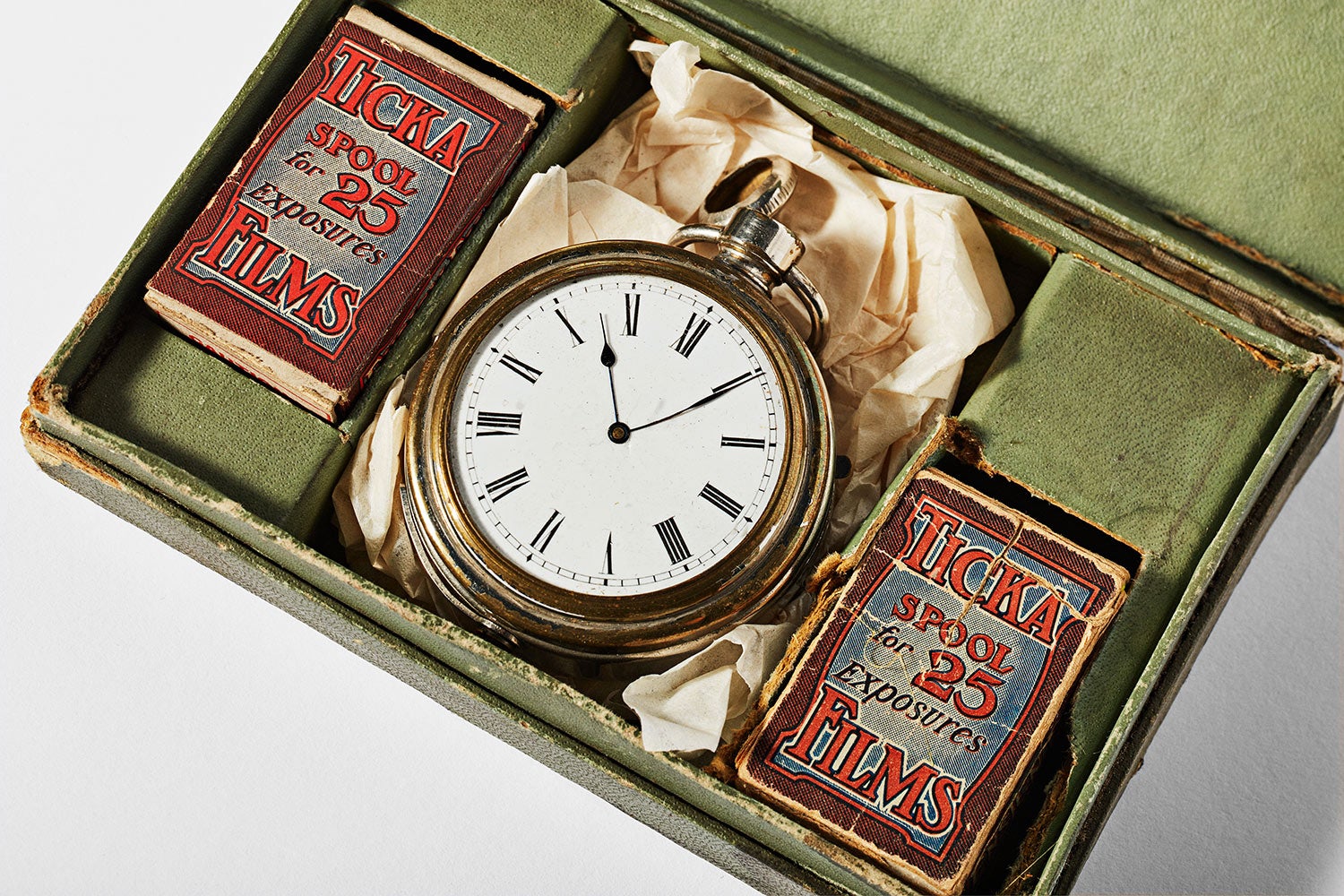

↑ The Ticka is just one of several watch-shaped cameras that the Eastman Museum has in its collection. The boxes to either side of the camera contain the film that was sold with it. The camera itself doesn’t have a traditional viewfinder to look through, so photographers would look down at the watch face. The hands form a V that represents the lens’s angle of view. Anything within that angle would show up in the photo.
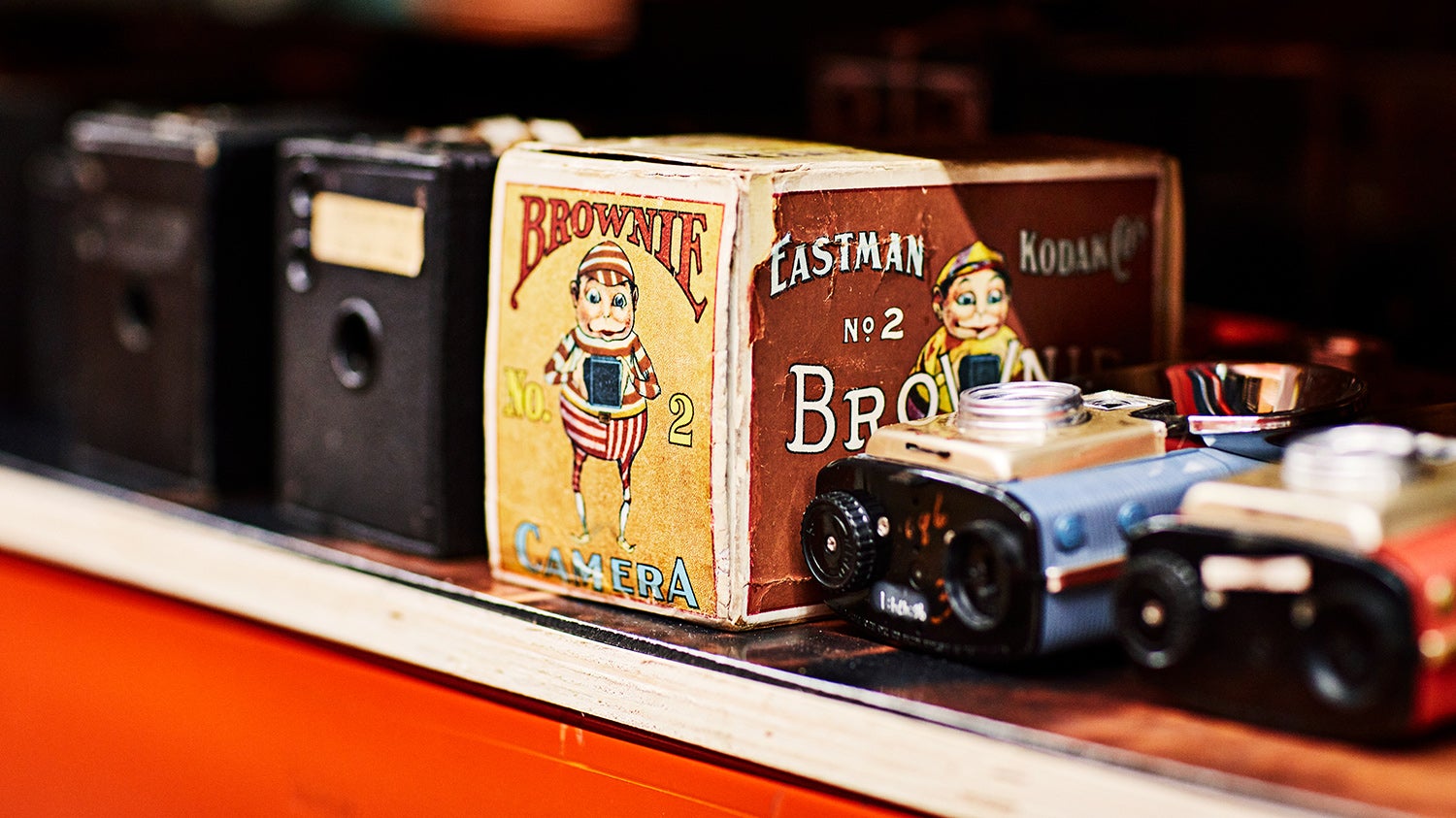

↑ While the Kodak represented the genesis of modern photography, the Brownie also played a crucial role. It debuted just 12 years after the original Kodak, but its $1 price tag ($36 in modern money) was a fraction of what the original Kodak cost. Kodak made dozens of versions of the Brownie, many of which you can still find out in the world right now. This original Brownie packaging gives a rare view of how the camera would have appeared on the shelf in the shop in the early 1900s. The Brownie Number 2 uses 120 roll film, a size that’s still available today.
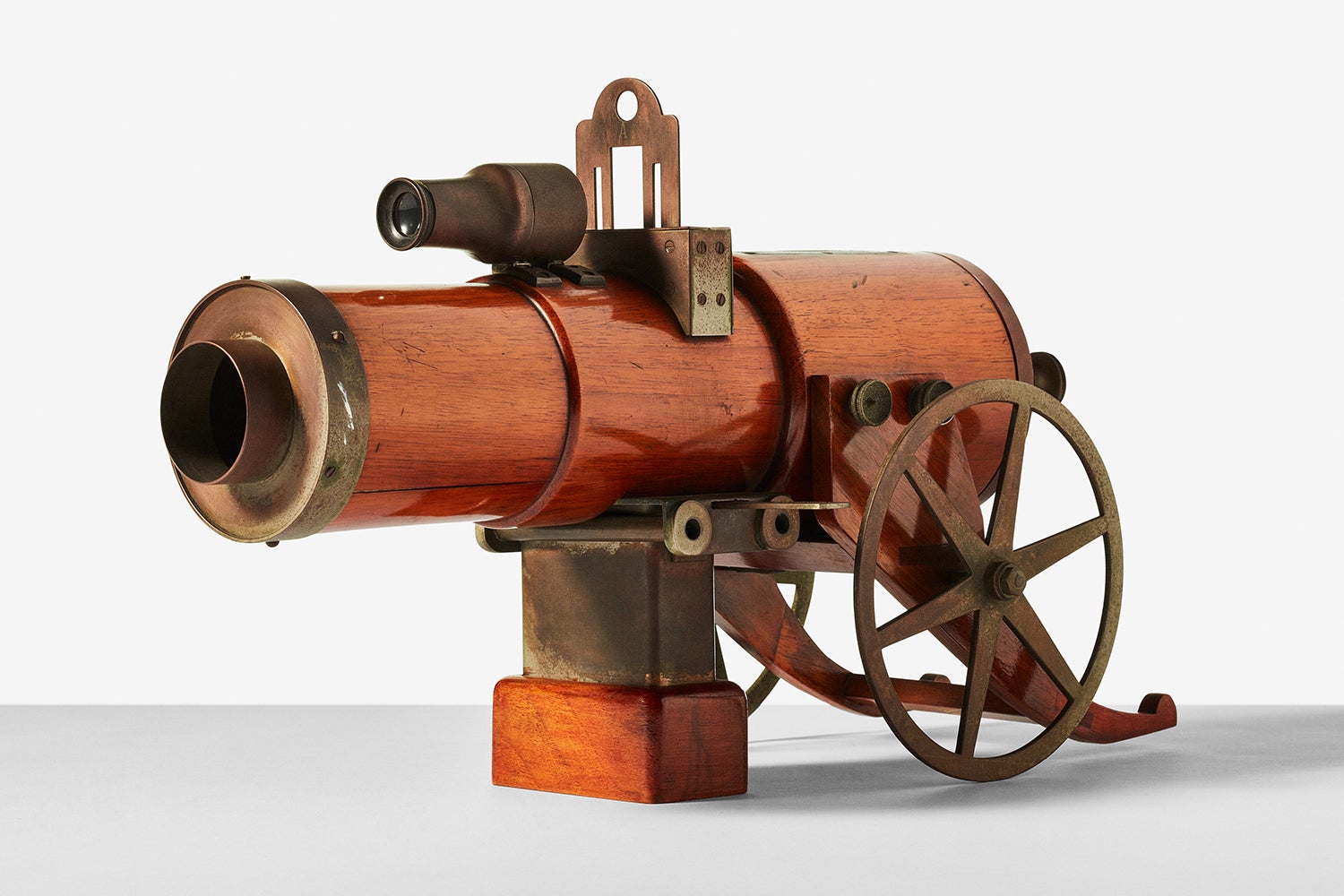

↑ There are roughly half-dozen Talbot Romain gun cameras left in the world. This is a fully functioning tintype camera. The tiny sensitized sheet went into the top of the barrel. Once the photographer took the photo, the plate would go into the small tank on which the camera rests for processing. The unique shape wasn’t essential to its function, but it did help photographers on the street lure in potential customers, who would walk away with a tiny tintype print once they had paid for their portrait.
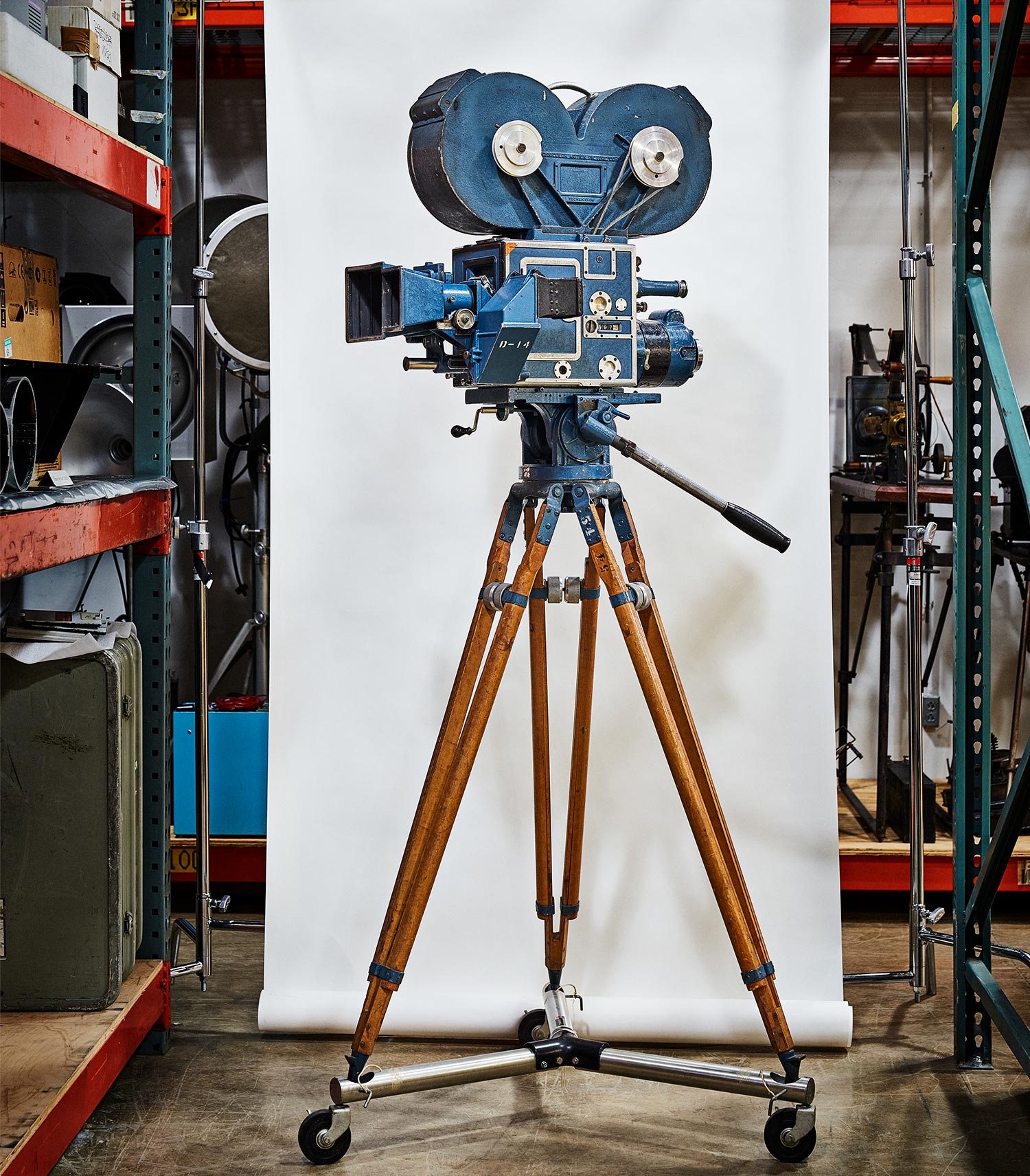

↑ This early Technicolor camera debuted in the early 1930s and shot the same image to three strips of black-and-white negatives at once through a prism. Cyan, yellow, and magenta filters made each roll of film sensitive to a specific part of the visible spectrum. Once the footage was shot, each roll was dyed a specific shade. When combined, they would create a full-color image. The technology collection includes a pair of these cameras that were used in the cinematography of some of the most iconic movies ever made, including The Wizard of Oz, Gone With the Wind, and even Star Wars.
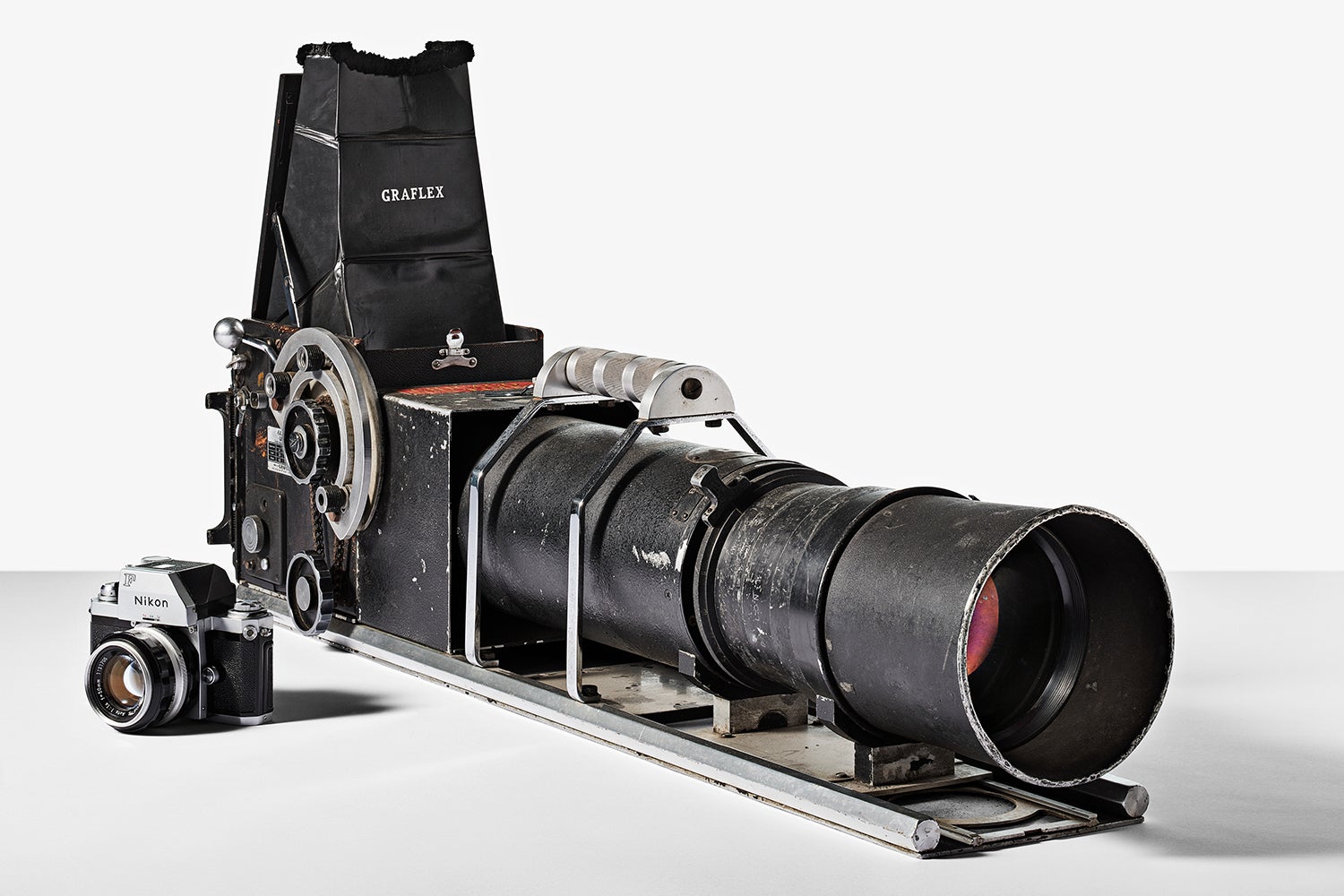

↑ This massive Graflex camera would have been right at home in the stands at a baseball game in the 1940s or ’50s. It’s an SLR, just like the relatively tiny Nikon F sitting next to it in the photo, just on a much larger scale. Moving the lever on the right of the camera would move the entire lens back and forth on a track to focus. Photographers could set stops along the focus path for specific distances so they could switch focus between bases in a hurry as the action unfolded.
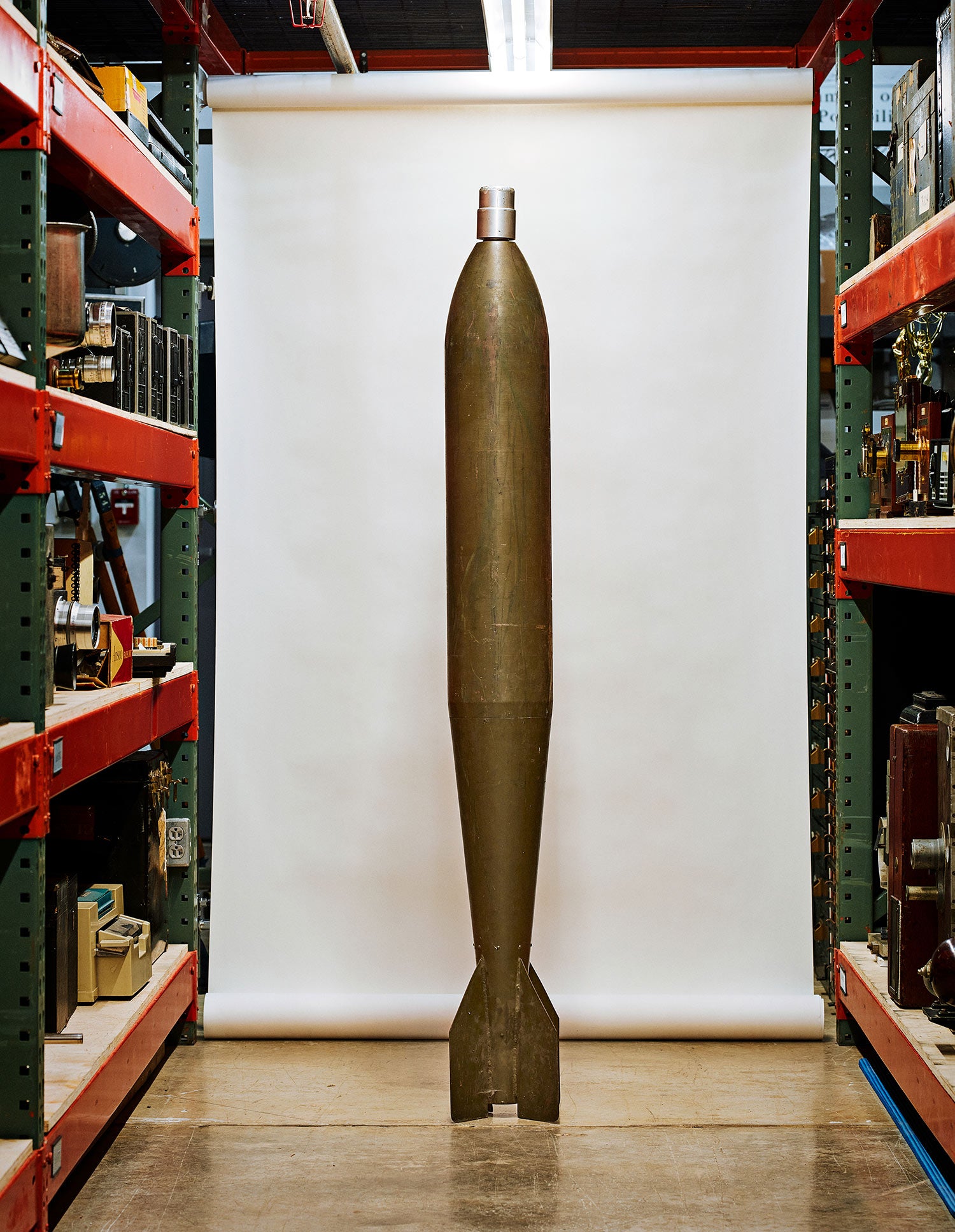

↑ This magnesium flash bomb stands nearly 6 feet tall and spends most of its time zip-tied to a support beam in the museum’s collection, even though all the flammable material has long been removed. The US armed forces used these in the 1930s for aerial reconnaissance. They would descend on a parachute, and at roughly 500 feet, the magnesium powder would ignite, creating enough light to illuminate the ground so aerial photographers could capture images that would otherwise be unobtainable.
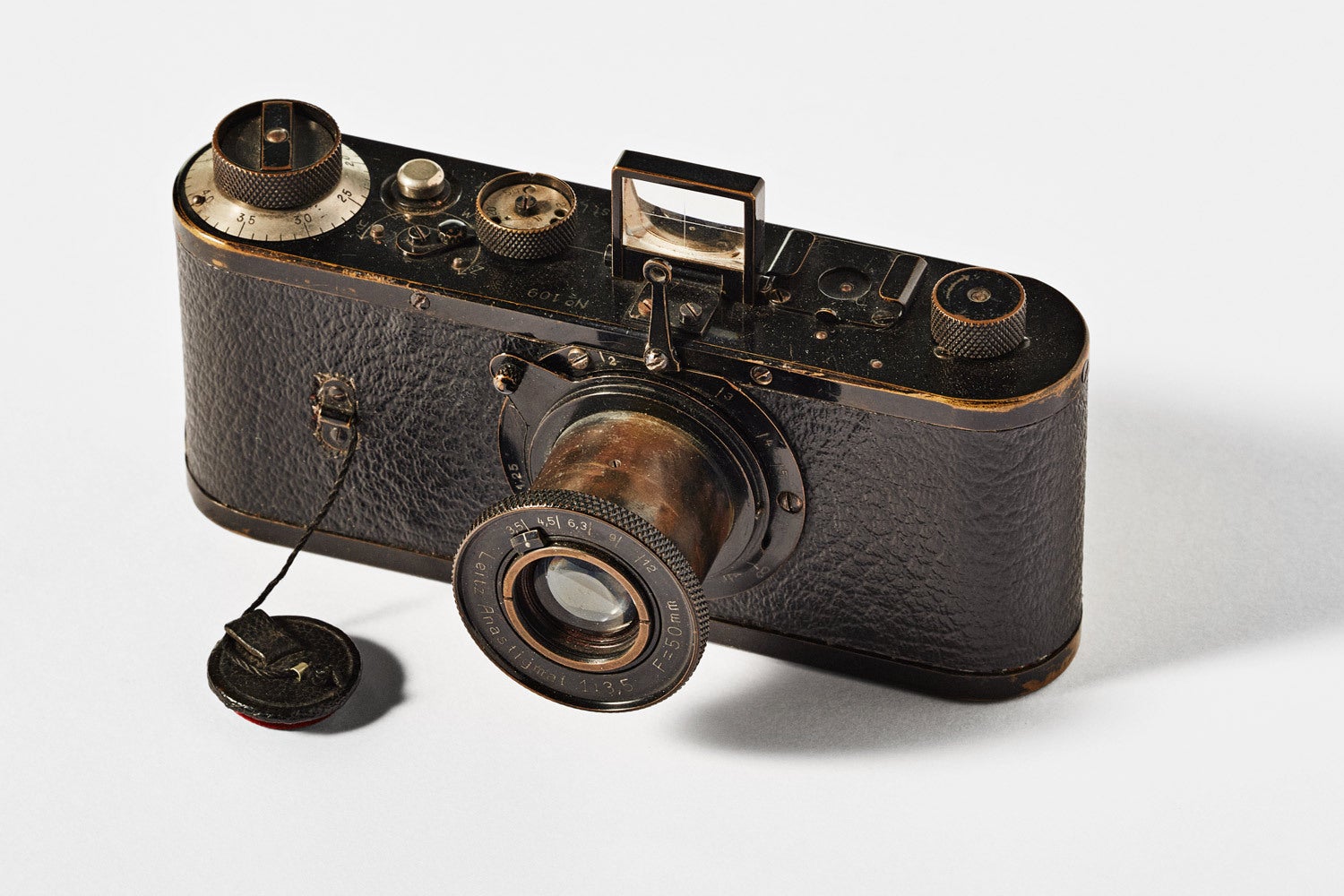

↑ Back in 1923, Leica produced just 22 prototypes as a trial run in the camera business. Roughly 12 of them have survived, many of which reside in private collections and all of which would fetch millions of dollars at auction. This is serial number 109 of the original production run. Number 105, which belonged to inventor Oscar Barnack himself, sold for $15 million back in 2022. The Eastman’s still works.
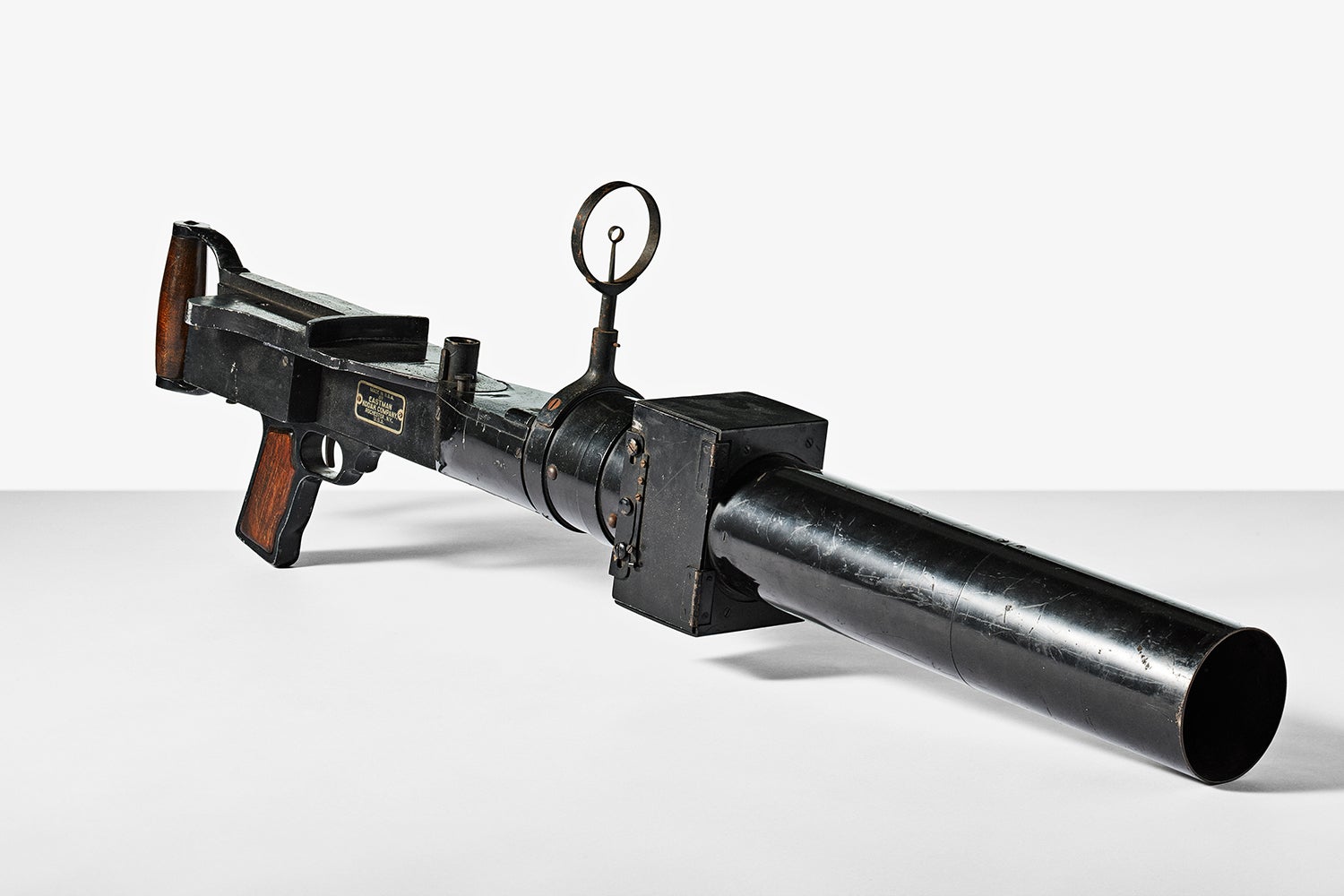

↑ Pilots in WWI didn’t have advanced simulators in which to practice dogfighting. Instead, they could use the Eastman Machine Gun camera, which was styled after a Lewis machine gun. Gunners could load a roll of common 120 film and then aim it just like a real gun. Once the film was processed, pictures with the enemy plane centered in the frame would be considered hits. It was a cheaper, safer way to practice than using live rounds.
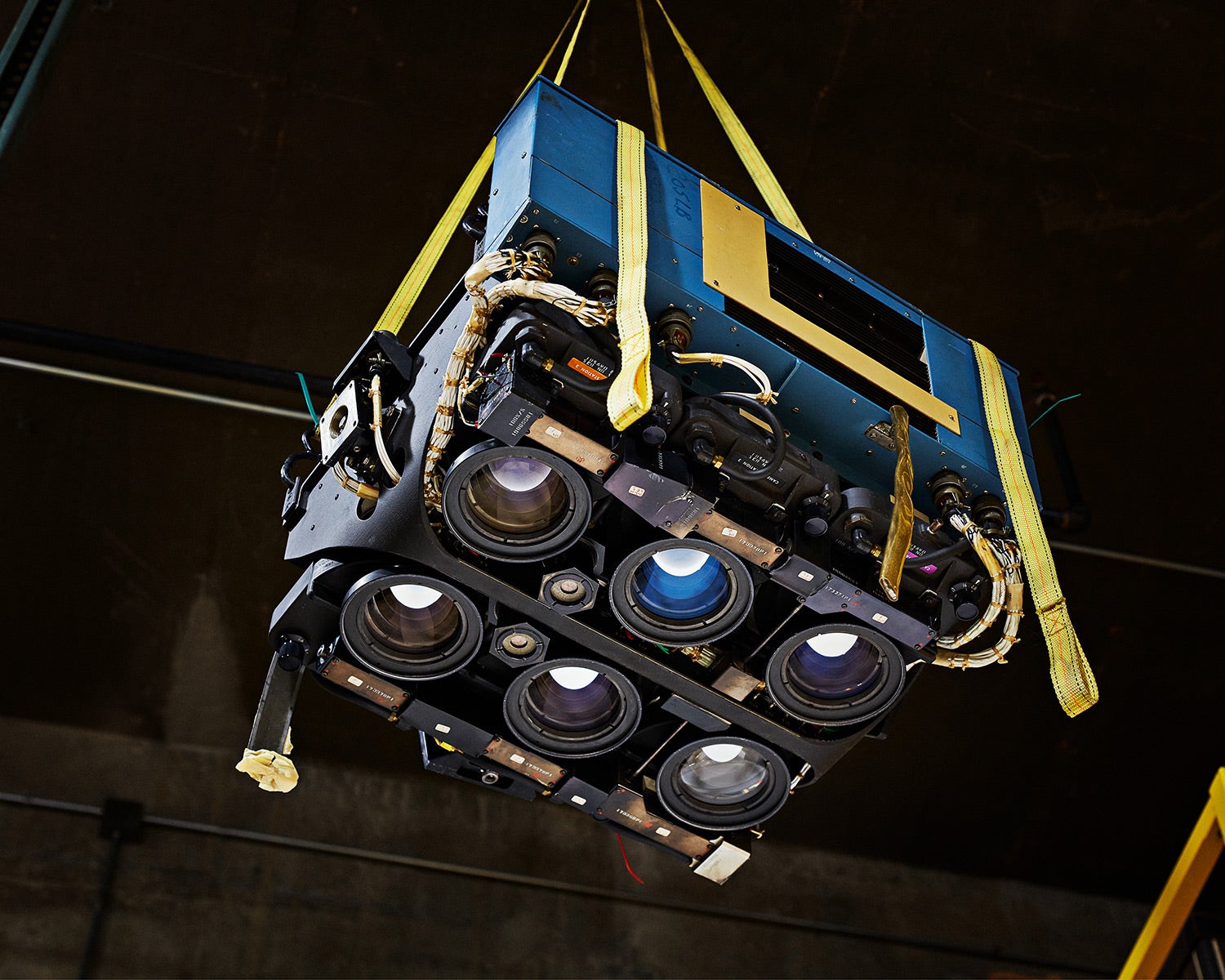

↑ Originally built as a backup camera for NASA’s Skylab space station in the 1970s, this rig found its use with the US Forest Service. Its six-camera array allowed aerial photographers to load six different kinds of film at once. The Forest Service used it to monitor the health of the landscape from above. It has six lenses, each with an independent film back so researchers could load several kinds of film all at once. The rig could shoot color, high-contrast black and white, and infrared all at the same time to observe different aspects of the scene.
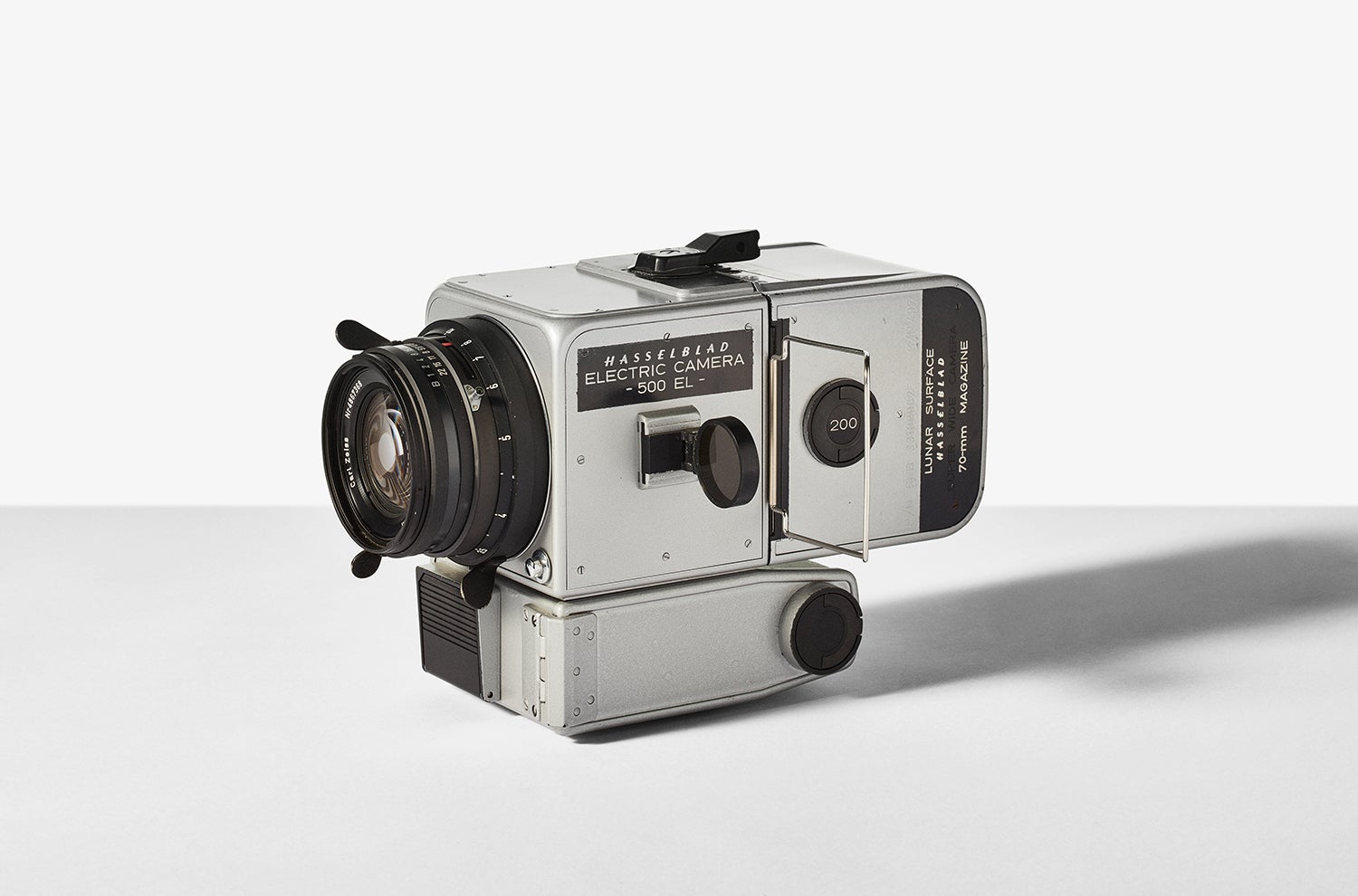

↑ There are several cameras very much like this Lunar Hasselblad sitting on the surface of the moon right now. It doesn’t look all that different from a typical 500 EL you’d find here on Earth, but it has a few astronaut-friendly modifications. The extra-large film back held far more shots than a typical roll, and the oversize handle on the dark slide (a simple piece of metal that blocks light when the camera isn’t in use) is big enough that astronauts could grab it with their bulky gloves.
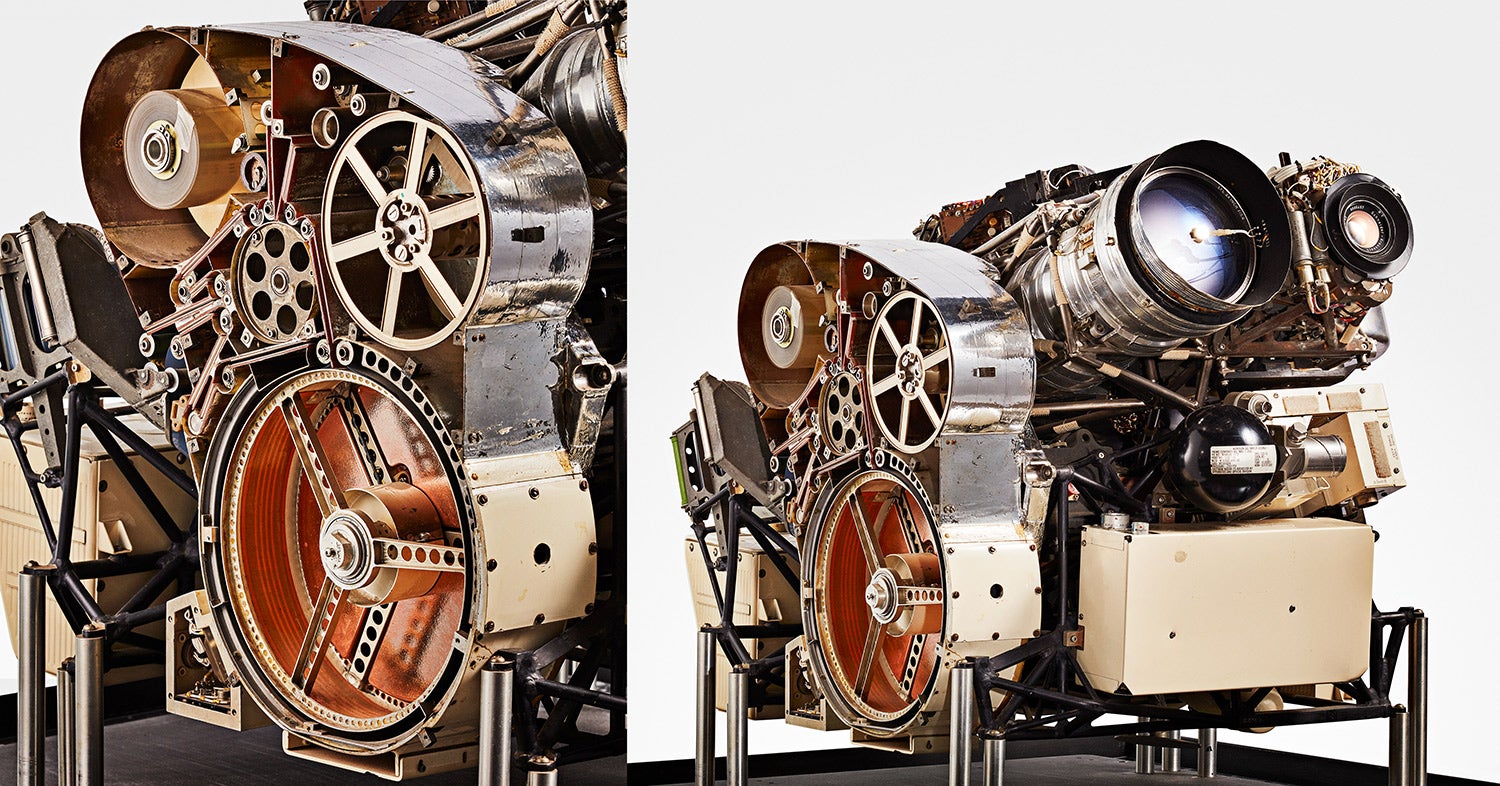
↑ In the mid 1960s, NASA sent a lunar orbiter exactly like this one (this is a spare that was ready for flight, but never needed) to photograph and catalog the entire surface of the moon in preparation for the 1969 landing. The module had two lenses: a wide-angle and a telephoto. It shot bimat film, which it developed and dried inside the device itself. It then made a scan of the image, which it beamed back to Earth in the form of a TV signal. The resulting images have some light and dark horizontal banding, but ultimately make up what’s still one of the most complete and detailed maps of the moon’s surface to date.
Read more PopSci+ stories.





